Arguably the most researched and tested supplement in history, creatine is a must for everyone who’s physically active. Only whey protein and caffeine come close in terms of the sheer number of peer-reviewed studies supporting its benefits.
Mounting evidence also suggests that creatine has benefits when it comes to cognition and memory, especially for aging people.
While you can get some creatine from your diet, you’ll see significant health benefits with additional supplementation.
I wouldn’t hesitate saying that creatine is probably the best supplement available. It’s something that all healthy people should take on a daily basis, but I should also stress that its greatest benefits occur when combined with resistance training.
What Is Creatine?
Creatine is a natural and perfectly safe substance that occurs in certain foods, particularly poultry, beef, pork, and seafood. It can also be synthesized in your liver and kidneys from the amino acids (the building blocks of protein) arginine, glycine, and methionine.
The main storage space for creatine is muscle tissue, where it works to increase energy and aids with recovery, among a number of other things.
What Does Creatine Do?
Creatine is an essential part of the so-called ATP-CP energy pathway. ATP stands for “adenosine triphosphate” and is known as the energy currency of the body. CP stands for “creatine phosphate.”
This energy pathway provides energy during short, high-intensity, and explosive bursts of exercise, such as sprinting, weight lifting, and jumping. For the first 2-3 seconds, it uses the ATP stored in your muscles.
Once the ATP is used up and has been transformed into ADP (adenosine diphosphate), creatine helps to recycle it back to ATP by adding a new phosphate group from the CP. This second process takes 6-8 seconds, after which other energy pathways take over.
So essentially, creatine recycles ATP, which provides a second quick round of energy, so to speak. The more creatine you have in your muscles, the more ATP can be recycled. It helps you exercise for a longer period of time.
Although your body can create creatine itself, and you can get some from food, your muscles are capable of storing much more than that. And this is why creatine supplementation is so popular and such a good idea.

Which Foods Contain Creatine?
Creatine is found in animal-based foods, such as the following:
- Beef
- Poultry
- Pork
- Salmon
- Herring
- Tuna
- Dairy
Because creatine occurs naturally in many animal products, vegetarians, vegans, and people who eat limited amounts of meat may benefit greatly from supplementation with creatine.
NOTE: Eggs contain only a negligible amount of creatine and are not considered a good natural source of creatine. However, they do contain the amino acid methionine, which is necessary for the body to synthesize creatine in the liver and kidneys. Therefore, eggs can indirectly help you produce creatine endogenously.

Creatine Has Amazing Exercise Performance Benefits
Supplementing with creatine—the best and cheapest form is creatine monohydrate—has been popular among professional athletes and serious exercisers for many years and it’s become more mainstream recently. And the benefits of creatine are, quite frankly, mind-blowing.
Its main benefit is overall sports performance. Creatine increases energy production in your muscles, improves post-exercise muscle recovery and growth, boosts your high-intensity exercise performance (sprinting, heavy weightlifting, and other short bursts of activity), and reduces muscle loss later in your life.
It also draws water into muscle tissue, improving overall body hydration. Because creatine increases water content in muscles, many people will see a slight increase in body weight on the scale. This body weight increase is purely due to that extra water and is really the only “negative” side effect of creatine.
On the flipside, because your muscles are more hydrated, they’ll also look bigger, which can actually be considered a benefit for most people. You’ll literally look a bit more toned.
Creatine Has Significant Neurological Benefits
Besides boosting exercise performance, creatine also has many neurological benefits.
Its cognitive benefits include better mental focus, enhanced memory function, and a positive role in various clinical conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
For healthy people, I recommend supplementing with 3-5 grams of creatine monohydrate every single day.
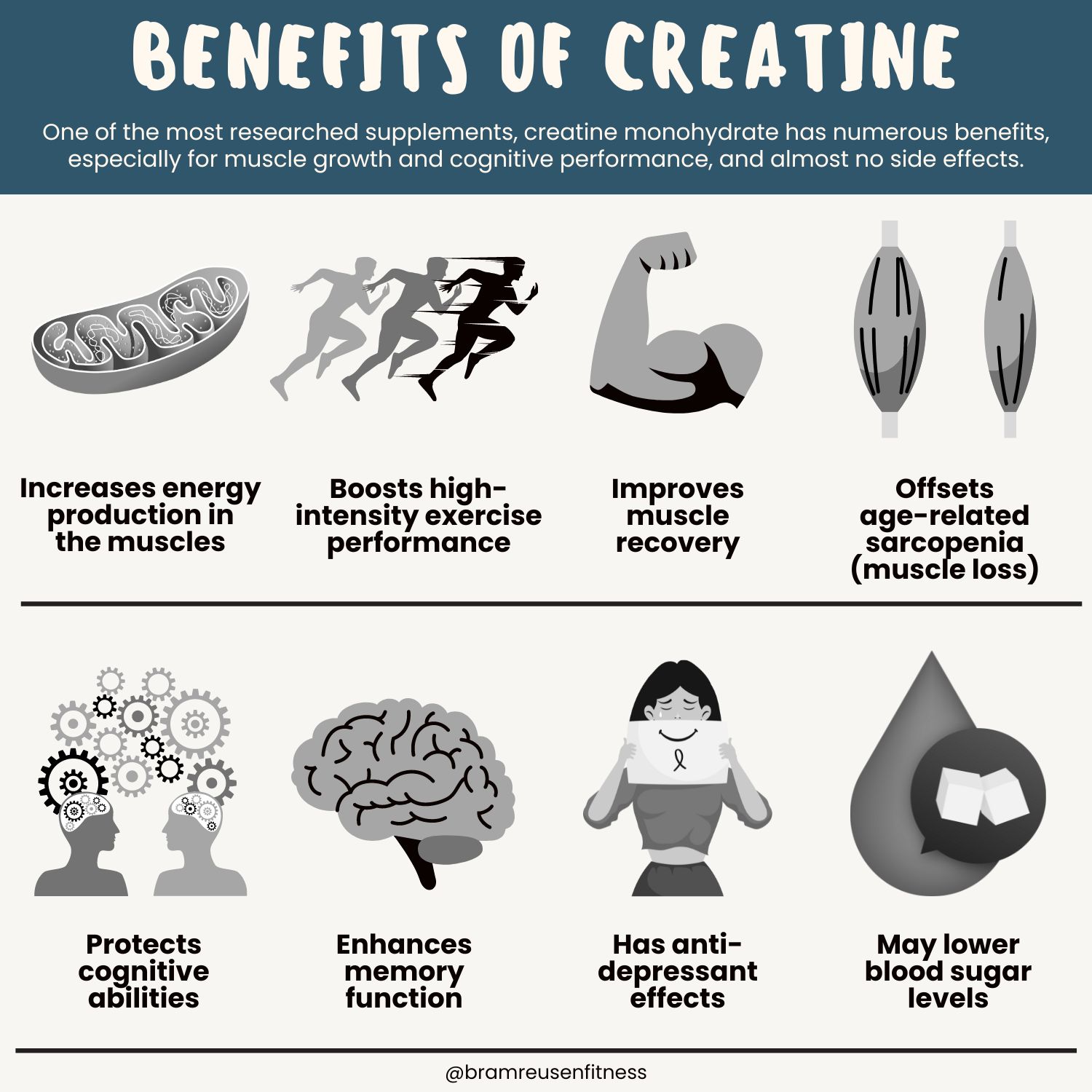
Benefits of Creatine
- Increases energy production in muscles
- Boosts high-intensity exercise performance
- Improves muscle recovery
- Offsets age-related sarcopenia (muscle loss)
- Protects cognitive abilities
- Enhances memory function
- Has anti-depressant effects
- May lower blood sugar levels






